
Malaysia
Indah Water Konsortium Data Breach
How Rhysida Ransomware Compromised Malaysia's National Sewerage Service
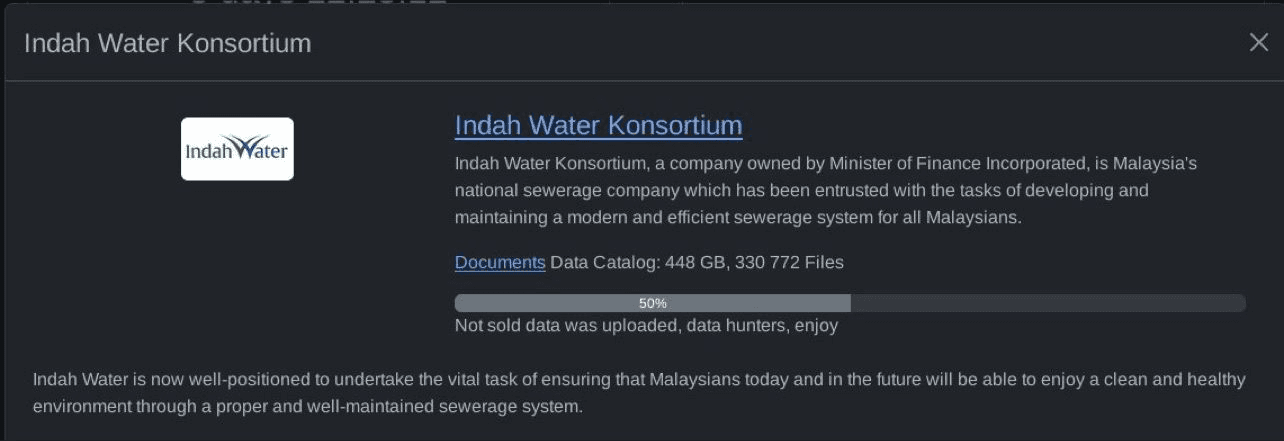
On November 7, 2023, Malaysia’s national sewerage company, Indah Water Konsortium (IWK), became the latest victim of the Rhysida ransomware group. Entrusted with developing and maintaining a modern sewerage system for millions of Malaysians, the attack on IWK compromised its operations, and most notably, exposed 448 GB of data, including sensitive information across 330,772 files.
The breach raises significant concerns about the vulnerabilities of critical infrastructure providers and their exposure to escalating ransomware threats.
The Breach Incident:
Rhysida Ransomware Attack
Victim: Indah Water Konsortium (iwk.com.my), owned by the Minister of Finance Incorporated
Date Discovered: November 8, 2023
Data Exposed: 448 GB of data, including 330,772 files
Threat Actor: Rhysida ransomware group
Leak Details:
50% of the stolen data was uploaded online, leaving the remaining half as a potential bargaining chip for attackers.
Files leaked included internal documents, potentially affecting Malaysia's national infrastructure and individuals connected to IWK's operations.
The stolen data was made available to data hunters, signaling the malicious actor's intent to monetize or further exploit the sensitive information.
Results and Consequences:
The ramifications of this breach extend beyond just the exposure of sensitive data. As a national sewerage provider, IWK’s operations are vital to public health and infrastructure. A disruption or leak of sensitive information in this sector poses risks including:
Compromise of Infrastructure Security: Leaked operational data could provide malicious actors with insights into critical infrastructure, increasing the risk of future attacks.
Public Trust Erosion: A breach of this magnitude not only threatens the security of IWK's internal operations but also undermines the public’s trust in national services.
Data Exploitation: Sensitive internal documents could be used for blackmail, fraud, or resold in secondary markets.
With half the data still unsold or unlisted, there’s a continuous threat of additional leaks, putting IWK in an ongoing state of risk.

Lessons Learned:
Critical Infrastructure Must Prioritize Cybersecurity:
Entities like IWK, responsible for vital national services, are prime targets for ransomware groups. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures such as network segmentation, regular penetration testing, and enhanced employee training are key to preventing such incidents.
Proactive Threat Monitoring:
The breach demonstrates the importance of continuous monitoring for early detection. Implementing automated threat exposure management solutions like Flawatch could have identified vulnerabilities or flagged unusual activity sooner, potentially minimizing the breach's impact.
Response Preparedness:
In the event of an attack, a well-orchestrated incident response plan ensures rapid containment. IWK’s breach underlines the need for rapid recovery and clear communication strategies post-breach to mitigate the long-term fallout.
Conclusion & Call to Action:
The attack on Indah Water Konsortium is a cautionary tale for organizations managing critical infrastructure. Proactive, automated security solutions like Flawatch can help identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. By investing in comprehensive threat management systems, companies can better protect themselves and their customers from evolving cyber threats.
Secure your infrastructure with Flawatch—before attackers make you their next target.
The Breach Incident:
Rhysida Ransomware Attack
Victim: Indah Water Konsortium (iwk.com.my), owned by the Minister of Finance Incorporated
Date Discovered: November 8, 2023
Data Exposed: 448 GB of data, including 330,772 files
Threat Actor: Rhysida ransomware group
Leak Details:
50% of the stolen data was uploaded online, leaving the remaining half as a potential bargaining chip for attackers.
Files leaked included internal documents, potentially affecting Malaysia's national infrastructure and individuals connected to IWK's operations.
The stolen data was made available to data hunters, signaling the malicious actor's intent to monetize or further exploit the sensitive information.

Results and Consequences:
The ramifications of this breach extend beyond just the exposure of sensitive data. As a national sewerage provider, IWK’s operations are vital to public health and infrastructure. A disruption or leak of sensitive information in this sector poses risks including:
Compromise of Infrastructure Security: Leaked operational data could provide malicious actors with insights into critical infrastructure, increasing the risk of future attacks.
Public Trust Erosion: A breach of this magnitude not only threatens the security of IWK's internal operations but also undermines the public’s trust in national services.
Data Exploitation: Sensitive internal documents could be used for blackmail, fraud, or resold in secondary markets.
With half the data still unsold or unlisted, there’s a continuous threat of additional leaks, putting IWK in an ongoing state of risk.

Lessons Learned:
Critical Infrastructure Must Prioritize Cybersecurity:
Entities like IWK, responsible for vital national services, are prime targets for ransomware groups. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures such as network segmentation, regular penetration testing, and enhanced employee training are key to preventing such incidents.
Proactive Threat Monitoring:
The breach demonstrates the importance of continuous monitoring for early detection. Implementing automated threat exposure management solutions like Flawatch could have identified vulnerabilities or flagged unusual activity sooner, potentially minimizing the breach's impact.
Response Preparedness:
In the event of an attack, a well-orchestrated incident response plan ensures rapid containment. IWK’s breach underlines the need for rapid recovery and clear communication strategies post-breach to mitigate the long-term fallout.
Conclusion & Call to Action:
The attack on Indah Water Konsortium is a cautionary tale for organizations managing critical infrastructure. Proactive, automated security solutions like Flawatch can help identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. By investing in comprehensive threat management systems, companies can better protect themselves and their customers from evolving cyber threats.
Secure your infrastructure with Flawatch—before attackers make you their next target.
The Breach Incident:
Rhysida Ransomware Attack
Victim: Indah Water Konsortium (iwk.com.my), owned by the Minister of Finance Incorporated
Date Discovered: November 8, 2023
Data Exposed: 448 GB of data, including 330,772 files
Threat Actor: Rhysida ransomware group
Leak Details:
50% of the stolen data was uploaded online, leaving the remaining half as a potential bargaining chip for attackers.
Files leaked included internal documents, potentially affecting Malaysia's national infrastructure and individuals connected to IWK's operations.
The stolen data was made available to data hunters, signaling the malicious actor's intent to monetize or further exploit the sensitive information.

Results and Consequences:
The ramifications of this breach extend beyond just the exposure of sensitive data. As a national sewerage provider, IWK’s operations are vital to public health and infrastructure. A disruption or leak of sensitive information in this sector poses risks including:
Compromise of Infrastructure Security: Leaked operational data could provide malicious actors with insights into critical infrastructure, increasing the risk of future attacks.
Public Trust Erosion: A breach of this magnitude not only threatens the security of IWK's internal operations but also undermines the public’s trust in national services.
Data Exploitation: Sensitive internal documents could be used for blackmail, fraud, or resold in secondary markets.
With half the data still unsold or unlisted, there’s a continuous threat of additional leaks, putting IWK in an ongoing state of risk.

Lessons Learned:
Critical Infrastructure Must Prioritize Cybersecurity:
Entities like IWK, responsible for vital national services, are prime targets for ransomware groups. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures such as network segmentation, regular penetration testing, and enhanced employee training are key to preventing such incidents.
Proactive Threat Monitoring:
The breach demonstrates the importance of continuous monitoring for early detection. Implementing automated threat exposure management solutions like Flawatch could have identified vulnerabilities or flagged unusual activity sooner, potentially minimizing the breach's impact.
Response Preparedness:
In the event of an attack, a well-orchestrated incident response plan ensures rapid containment. IWK’s breach underlines the need for rapid recovery and clear communication strategies post-breach to mitigate the long-term fallout.
Conclusion & Call to Action:
The attack on Indah Water Konsortium is a cautionary tale for organizations managing critical infrastructure. Proactive, automated security solutions like Flawatch can help identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. By investing in comprehensive threat management systems, companies can better protect themselves and their customers from evolving cyber threats.
Secure your infrastructure with Flawatch—before attackers make you their next target.
The Breach Incident:
Rhysida Ransomware Attack
Victim: Indah Water Konsortium (iwk.com.my), owned by the Minister of Finance Incorporated
Date Discovered: November 8, 2023
Data Exposed: 448 GB of data, including 330,772 files
Threat Actor: Rhysida ransomware group
Leak Details:
50% of the stolen data was uploaded online, leaving the remaining half as a potential bargaining chip for attackers.
Files leaked included internal documents, potentially affecting Malaysia's national infrastructure and individuals connected to IWK's operations.
The stolen data was made available to data hunters, signaling the malicious actor's intent to monetize or further exploit the sensitive information.

Results and Consequences:
The ramifications of this breach extend beyond just the exposure of sensitive data. As a national sewerage provider, IWK’s operations are vital to public health and infrastructure. A disruption or leak of sensitive information in this sector poses risks including:
Compromise of Infrastructure Security: Leaked operational data could provide malicious actors with insights into critical infrastructure, increasing the risk of future attacks.
Public Trust Erosion: A breach of this magnitude not only threatens the security of IWK's internal operations but also undermines the public’s trust in national services.
Data Exploitation: Sensitive internal documents could be used for blackmail, fraud, or resold in secondary markets.
With half the data still unsold or unlisted, there’s a continuous threat of additional leaks, putting IWK in an ongoing state of risk.

Lessons Learned:
Critical Infrastructure Must Prioritize Cybersecurity:
Entities like IWK, responsible for vital national services, are prime targets for ransomware groups. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures such as network segmentation, regular penetration testing, and enhanced employee training are key to preventing such incidents.
Proactive Threat Monitoring:
The breach demonstrates the importance of continuous monitoring for early detection. Implementing automated threat exposure management solutions like Flawatch could have identified vulnerabilities or flagged unusual activity sooner, potentially minimizing the breach's impact.
Response Preparedness:
In the event of an attack, a well-orchestrated incident response plan ensures rapid containment. IWK’s breach underlines the need for rapid recovery and clear communication strategies post-breach to mitigate the long-term fallout.
Conclusion & Call to Action:
The attack on Indah Water Konsortium is a cautionary tale for organizations managing critical infrastructure. Proactive, automated security solutions like Flawatch can help identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. By investing in comprehensive threat management systems, companies can better protect themselves and their customers from evolving cyber threats.
Secure your infrastructure with Flawatch—before attackers make you their next target.






Get Started
Demo the hacker's prespective
All we need is your business email and 10 minutes to introduce you to our platform.

Continuously watching out for security flaws

Continuously watching out for security flaws

Continuously watching out for security flaws

Continuously watching out for security flaws


